Infrared thermal imaging makes it impossible for the human eye to directly see the surface temperature distribution of the target, and becomes a thermal image representing the temperature distribution of the target surface that can be seen by the human eye. The development of infrared technology has increased the human senses from five to six.
Government regulation, public concern for the environment, personnel safety and economic considerations make the leakage of hydrocarbons and other gases the top priority in today's energy industry. Most industrial gases and chemicals are invisible to the naked eye.
Companies in the energy industry use a variety of tools to monitor, identify, and control these compounds in the upstream exploration and production processes, downstream refining and distribution processes, and transportation.
Infrared imaging allows workers to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are invisible to the human eye. Infrared cameras can visualize leaked gas. Emissions that are usually odorless and invisible are also toxic or flammable.
More specifically, mid-wave infrared (MWIR) cameras are spectrally optimized to image at the peak absorption wavelength of many VOCs. Optical gas imaging is a proven technology to detect dangerous and expensive gas leaks. Optical gas imaging technology has been successfully applied in many industries such as oil refining, chemical engineering, petroleum and petrochemicals, etc., helping to improve the safety of the construction environment and prevent high losses due to production stoppages.
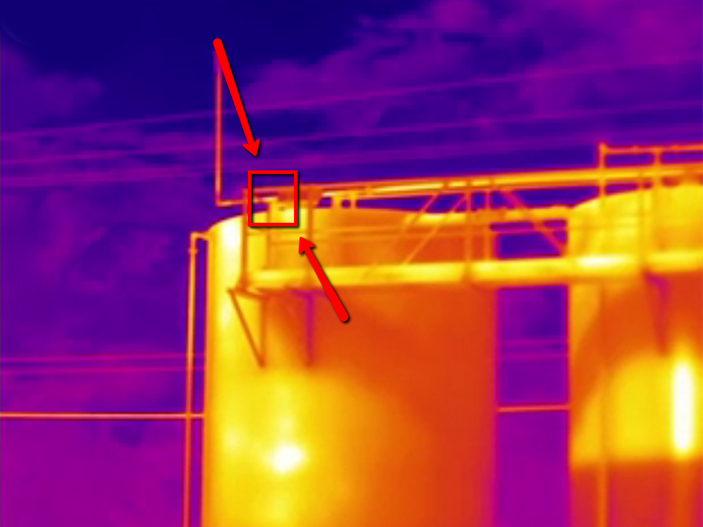
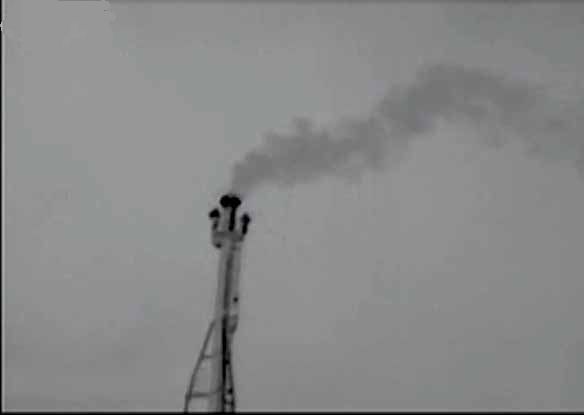


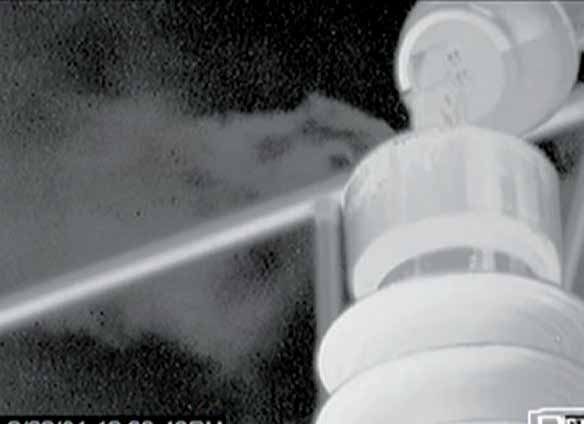
Currently the most widely used is the use of handheld devices to identify these fugitive emissions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends that by using optical gas imaging (OGI) technology, companies can increase the number of detectable devices, thereby reducing the cost of identifying leaks. It is vital that companies can understand the status of the plant as completely as possible to improve safety, efficiency, profitability, and accountability to the environment.
TIM HC Series Refrigerated Medium Wave Infrared Thermal Imager, a MWIR OGI core, can detect and provide real-time images of fugitive emissions. Unorganized emissions lead to safety issues, economic losses, air pollution and climate change. The entire scanning area can be continuously monitored throughout the day. It provides a complete picture of all devices at once, and the leak is shown as "smoke" when viewed on a computer monitor。
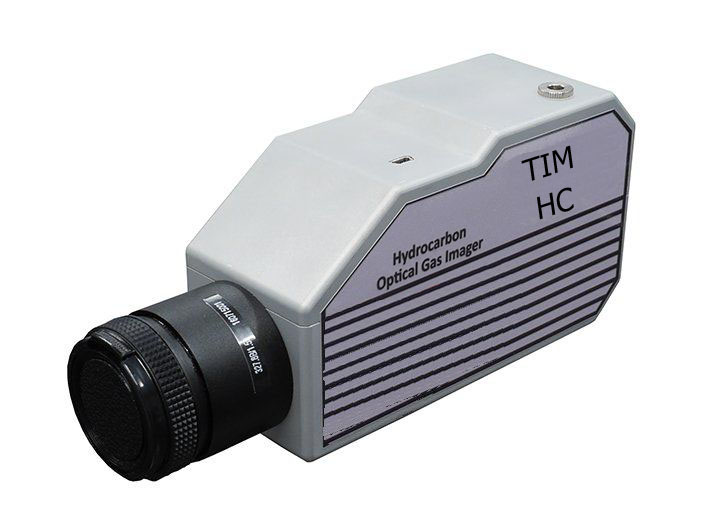

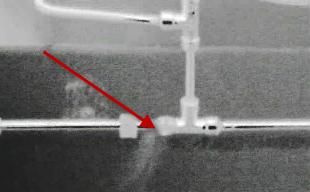
Gas detection imagers are a good way to visualize gases by using the physical principles of leaking gases. The imager will take a panoramic view of the scanning area and indicate the presence of a leak in the form of smoke on its viewfinder or LCD screen. The key factors for the success of optical gas imagers today are safety, efficiency and profitability.。
First, the gas detection imager is a fast, non-contact measuring instrument that can be used in hard-to-reach places. It can detect small leaks a few meters away and large leaks a few hundred meters away. In this way, the operator does not need to approach the leak, which significantly improves safety.
A factory may have thousands of connections and accessories that need to be checked regularly, but the reality is that less than one percent of these parts will leak. Testing them with traditional “sniffers” takes a lot of time and effort. Using a sniffer or probe is time-consuming, and much of the time is wasted on checking for a leak-free device. The gas detection imager can provide complete images and immediately eliminate areas that do not require any manipulation. This means huge savings in time and manpower.
Another advantage is that the system does not need to shut down the equipment during the inspection, which can save a lot of money (sometimes up to 30,000 euro per day or per device).
Gas imagers are an effective way to detect leaks in the workplace. This is especially useful in foundries for automotive parts such as gearboxes or brake discs. In many metal castings and metal hardening processes, large amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) are produced. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that usually forms during combustion. Workers on charging stations or narrow aisles inadvertently inhale this colorless, odorless gas in large quantities, causing workers to suddenly lose consciousness. At higher concentrations, it may even be fatal without any signs.

